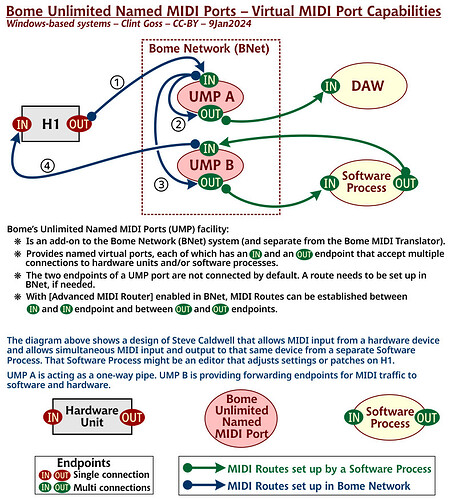
In order to route in to in our out to out you need to turn Advanced MIDI Router in the Setting (Cog Icon)

I just did it the way it made sense to me. The more virtual ports you add, the more routes you need to have, so I only created two.
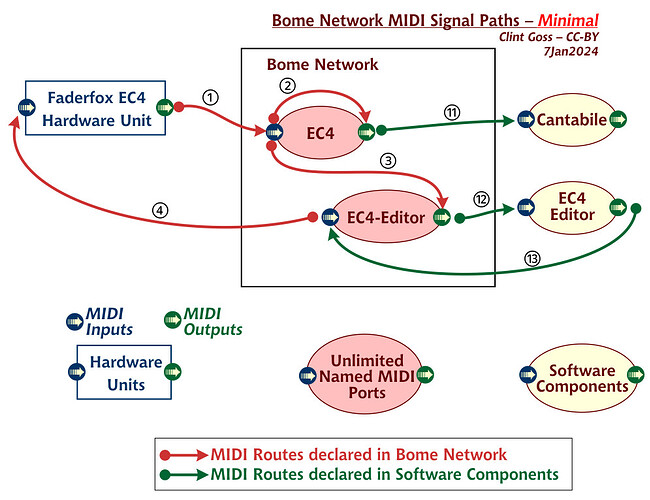
Here is a writeup I did when analyzing Bome Network before it was released. I periodically refer to it to keep my head on straight. I’m not sure if it is 100% accurate but for now this is what I use unless something trips me up.
Bome Unlimited Virtual MIDI ports are really just connectors or endpoints. Without routing, they actually do nothing as they are connectors to ‘nowhere’.
You need to use the Bome Network Router to make them actually useful by creating MIDI routes between the connectors and put real devices or applications on one end of a given connector.
The below is a summary of my discovery while experimenting with them:
INPUT to OUTPUT
When you create a Bome Virtual MIDI point you create two endpoints. One for INPUT and one for OUTPUT.
You can route the input of one port to the output of the same port to create a one way pipe. For instance if you have INPUT ‘A’ routed to OUTPUT ‘A’. Then with your application you can send MIDI to INPUT ‘A’ and whatever you send there will be also seen on OUTPUT ‘A’.
You can also direct two inputs to a single output with 2 routes. For instance if you have INPUT ‘A’ routed to OUTPUT ‘A’ and OUTPUT ‘B’, whatever MIDI comes in to INPUT ‘A’ will be seen on both OUTPUT ‘A’ and OUTPUT ‘B’.
INPUT to INPUT
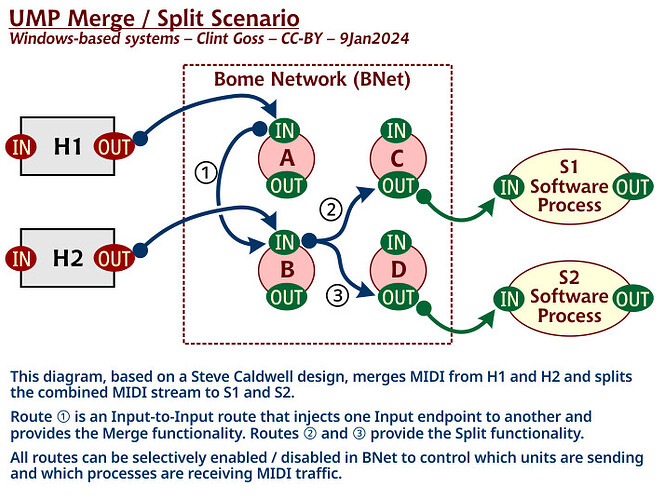
Another thing you can do is direct an INPUT to another INPUT. This could be handy if you want to inject an input from one input port to another. You can then route the initial destination ports to other ports, creating a MIDI split function that can quickly be turned on and off with by checking or un-checking a given routing.
Example:
Route 1 - IN: A Virtual In ->IN: B Virtual In
Route 2 - IN: B Virtual In → OUT: C Virtual Out
Route 3 - IN: B Virtual In → OUT: D Virtual out
In the above, anything coming into either A or B will be sent to C and D. However, you could turn off Route 1 and then only B will be sent to C and D. A will essentially be turned off allowing only B to be split to C and D.
OUTPUT to INPUT
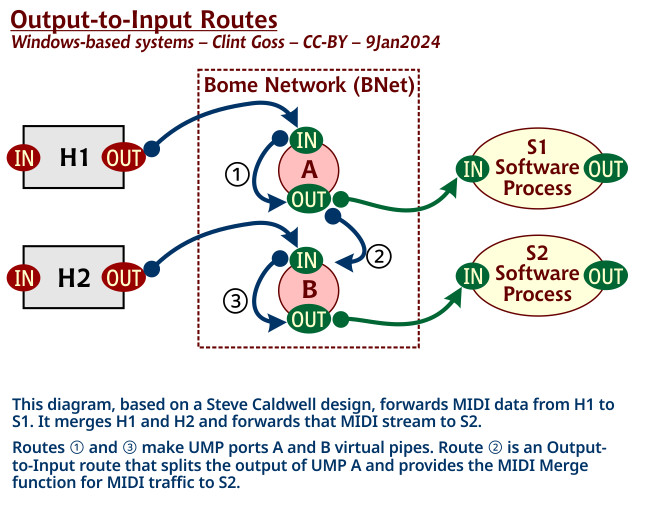
This is used for injecting an existing output port’s data into a different input connector (virtual ports only). You can take the output of one port and direct it to the input of another port.
Example
Route 1 - IN: A Virtual In → OUT: A Virtual Out - MIDI pipe as explained earlier
Route 2 - OUT: A Virtual Out → IN: B Virtual In
Route 3 - IN: B Virtual In - > OUT: B Virtual Out - MIDI pipe as explained earlier
Anything coming from input A will go to output A and input B which in turn will go to Output B. Anything coming from input B will only go to output B. Essentially we get a split on input from A (to A and B) and a pipe from B (B to B)
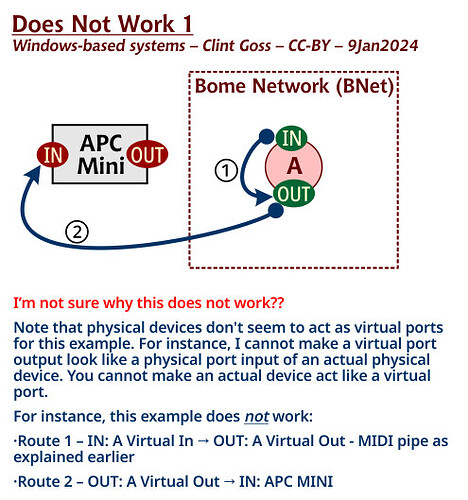
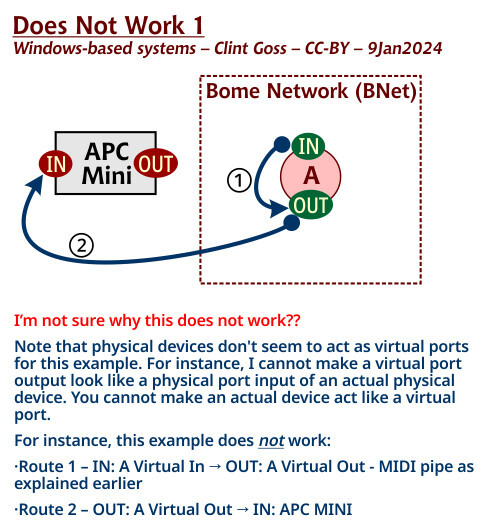
Note, that physical devices don’t seem to act as virtual ports for this example. For instance I cannot make a virtual port output look like a physical port input of an actual physical device. You cannot make actual device act like a virtual port.
For instance, the below example does not work:
Route 1 - IN: A Virtual In → OUT: A Virtual Out - MIDI pipe as explained earlier
Route 2 - OUT: A Virtual Out → IN: APC MINI
Rather you should do this:
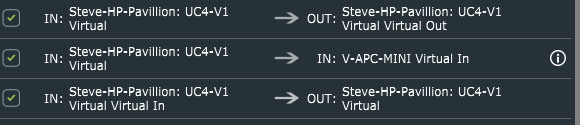
Route 1 - IN: A Virtual In → OUT: A Virtual Out - MIDI pipe as explained earlier
Route 2 - OUT: A Virtual Out → IN: Virtual APC MINI
Route 3 - IN: Virtual APC MINI → OUT: Virtual APC MINI - MIDI pipe as explained earlier
Route 4 … - IN: Virtual APC MINI → OUT: (Any other destination)
Or you could do this to achieve the same result (but not represented as output to input) See OUTPUT to OUTPUT Below:
Route 1 - IN: A Virtual In → OUT: A Virtual Out - MIDI pipe as explained earlier
Route 2 - OUT: A Virtual Out → OUT Virtual APC MINI
OUTPUT to OUTPUT
You can duplicate output ports in this configuration essentially providing a MIDI split function
Example
Route 1 - IN: A Virtual In → OUT: A Virtual Out - MIDI pipe as explained earlier
Route 2 - OUT: A Virtual Out → OUT: APC MINI
Route 3 - OUT: APC MINI → OUT: BMT 1
Route 2 above creates a new output to my attached APC MINI device. Everything coming in Virtual Port A (which is a Pipe to Virtual Port A Output) will go to my APC MINI
Route 3 will also send anything that is going to the APC MINI to BMT 1 Output
In summary:
When the source is input and destination is output you create a 1 way pipe
When destination is input you are injecting the MIDI data from the source (input or output) to the endpoint. This appears to only work with Virtual MIDI ports if you are injecting to a destination input.
When the source and destination are outputs you are essentially duplicating existing ports to allow for a MIDI split function.
It appears that the quickest way to get a MIDI merge function is to take multiple existing INPUTS as a source and route to a single OUTPUT as a destination.
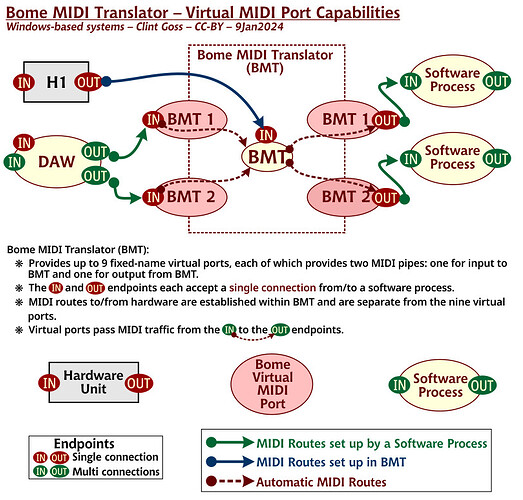
NOTE: This all appears NOT to work correctly with BMT Ports if used with Bome MIDI Translator PRO since BMT ports cannot be routed between themselves and one and only one end of a BMT port connection must be MT Pro while the other end must not.
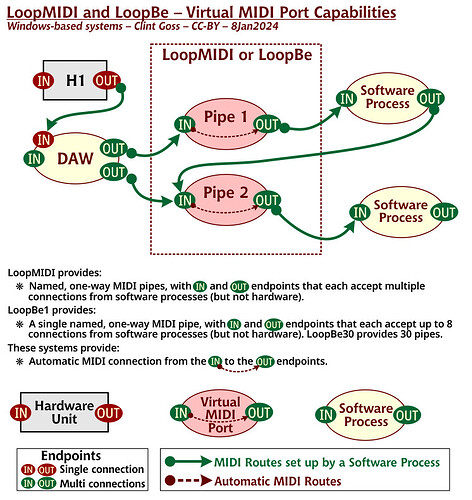
Also virtual MIDI ports generated by other applications such as LoopMIDI or LoopBE may behave different as most appear to be MIDI pipes.
There are limitations when including physical ports into the mix as described above. Best to create virtual port connections with the physical ports and use applications with the virtual port connectors only. Attempting to inject into a physical port input does not seem to work, although routing signal to output does.
Steve Caldwell
Bome Customer Care
Also available for paid consulting services: bome@sniz.biz